In 2025, as interest rates stabilize and markets recover from recent volatility, many investors are reevaluating their strategies. According to recent forecasts, the U.S. real estate sector is poised for gradual improvement in 2026, with home sales potentially jumping 14% and commercial investment volumes rising amid easing financing conditions. Whether you’re a beginner dipping your toes into real estate, a residential landlord seeking higher yields, or a high-net-worth individual aiming for real estate portfolio diversification, the debate of commercial vs. residential property investing remains central.
This article breaks down the key differences, pros, cons, and outlook for 2026. We’ll explore factors like rental yield, cap rates, tenant turnover, and market volatility to help you decide which path aligns with your capital, risk tolerance, and goals. No one-size-fits-all answer exists—residential often suits hands-on beginners, while commercial appeals to those chasing passive income through structures like triple net leases (NNN). Let’s dive in.
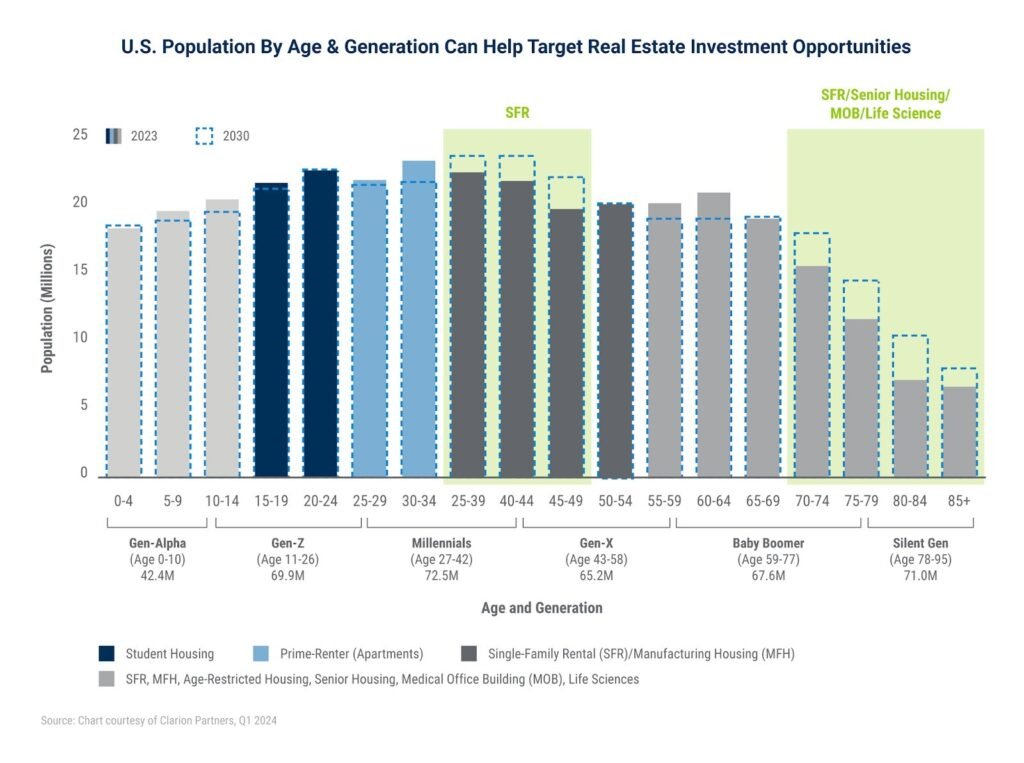
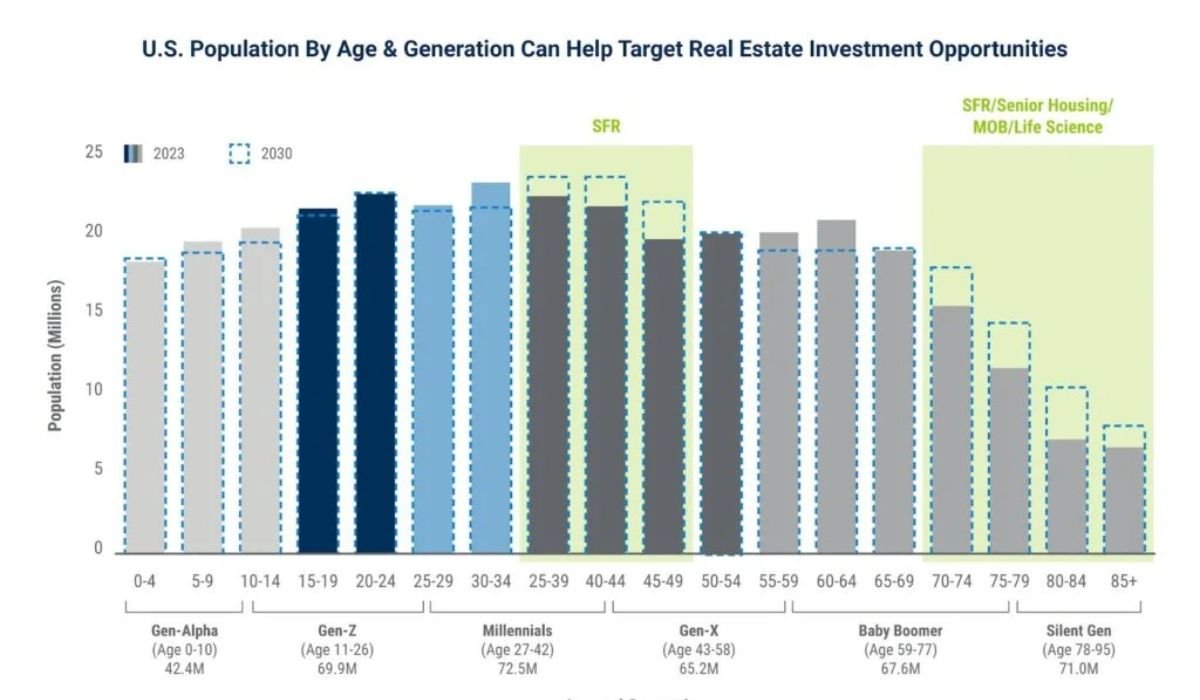
Analyzing Demographics to Target Real Estate Investment …
Understanding Residential Property Investing
Residential investing involves properties like single-family homes, duplexes, or multifamily units rented to individuals or families. It’s the most accessible entry point for many, especially beginners.
Imagine buying a four-unit apartment building in a growing suburb—tenants pay rent monthly, covering your mortgage while building equity. This is classic residential investing: steady demand driven by housing needs.
Key Advantages
- Lower entry barriers: Beginners can start with FHA loans requiring as little as 3.5% down, making it ideal for best real estate investment for beginners.
- Stable demand: People always need homes. In 2026, forecasts predict strong renter demand due to affordability challenges in buying, boosting occupancy in multifamily units.
- Easier management for starters: Property management is straightforward; many handle it themselves initially or hire affordable services.
- Appreciation potential: Neighborhood improvements (schools, amenities) drive value growth.
Potential Drawbacks
- Higher tenant turnover: Annual leases mean more vacancies and turnover costs.
- Hands-on involvement: Repairs and tenant issues fall on you unless outsourced.
- Lower yields in some markets: Rental yield averages 5-8%, often lower than commercial.
For 2026, residential looks promising. Multifamily vacancy is expected to stabilize, with rent growth accelerating as new supply shrinks dramatically—starts could drop over 50% from peaks.

Exploring Commercial Property Investing
Commercial properties include offices, retail spaces, industrial warehouses, or strip malls leased to businesses. Think triple net leases (NNN) where tenants cover taxes, insurance, and maintenance—true passive income.
Key Advantages
- Higher potential returns: Cap rates often range 6-10%, outperforming residential in stable sectors.
- Longer lease duration: 5-10+ year leases reduce tenant turnover and provide predictable cash flow.
- Tenant pays expenses: In NNN setups, your outgoings are minimal.
- Inflation hedge: Rents often escalate annually.
Potential Drawbacks
- Higher capital requirements: Larger down payments and stricter commercial real estate financing vs residential loans.
- Economic sensitivity: Tied to business health; higher market volatility.
- Complex management: Navigating zoning laws and negotiations requires expertise.
- Vacancy risks: One tenant leaving can hit income hard.
In 2026, commercial shows selective strength. Industrial and retail remain resilient, while office faces challenges but opportunities in premium assets.

Key Differences: A Side-by-Side Comparison
To make an informed choice in commercial vs. residential property investing, consider these core distinctions:
- Returns and Yields: Commercial often boasts higher cap rates and rental yield, especially in NNN deals. Residential shines in appreciation but may lag in immediate cash flow.
- Lease Terms and Tenants: Commercial: Longer leases, business tenants (credit checks vital). Residential: Shorter leases, higher tenant turnover.
- Financing: Residential loans are easier and cheaper; commercial requires more scrutiny and equity.
- Management and Risks: Residential can be DIY-friendly but hands-on. Commercial offers passivity but higher risks of commercial property vs residential in downturns.
- Market Influences: Residential tracks population and jobs; commercial ties to economic cycles.
| Aspect | Residential | Commercial |
| Typical Cap Rate (2025-2026 est.) | 4-7% | 6-10% (varies by sector) |
| Lease Duration | 1-2 years | 5-15 years |
| Tenant Turnover | High | Low |
| Passive Income Potential | Moderate (self-manage or hire) | High (e.g., NNN leases) |
| Entry Capital | Lower | Higher |
| Volatility | Lower | Higher (economic-dependent) |
READ ALSO: Real Estate Market Trends in 2026: What Buyers, Sellers, and Investors Should Expect
2026 Outlook: Trends Shaping Both Sectors
As we head into 2026, recovery signals emerge. Interest rates are expected to ease slightly, boosting activity. Residential forecasts a sales surge from pent-up demand, while commercial sees investment growth in living sectors and industrials.
Residential Highlights
Strong multifamily fundamentals as supply tightens. Ideal for passive income property strategies via rentals.
Commercial Highlights
Opportunities in retail and industrial; caution in office. Distressed assets may offer entry points.
Commercial vs residential property investing ROI 2025-2026: Both viable, but diversification wins—many blend for balance.
Risks and Considerations
Both face market volatility, but commercial amplifies in recessions. Mitigate with reserves and due diligence. Transitioning from residential to commercial real estate? Start small, partner with experts.
Which Is Best for You in 2026?
It depends on you. Beginners: Start residential for lower barriers. Scaling landlords: Commercial for higher yields and passivity. Diversifiers: Mix both.
No perfect choice—align with your risk tolerance and capital. In 2026’s improving market, informed action beats waiting.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE: A Beginner’s Guide to Property Investment: Step-by-Step