Imagine navigating a bustling city where traffic flows seamlessly, energy is conserved intelligently, and public safety alerts arrive in real-time—preventing disasters before they escalate. This isn’t a distant dream; it’s the reality unfolding through smart infrastructure: IoT in Cities. As urban populations swell to unprecedented levels, cities face mounting pressures from congestion, resource scarcity, and climate vulnerabilities. This article explores how the Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing urban living by creating resilient, connected systems that enhance efficiency and sustainability. We’ll delve into the tangible benefits for stakeholders like urban planners and municipal IT directors, outline a practical roadmap for implementation, and address common challenges—all while balancing cutting-edge technology with budget realities. Whether you’re optimizing public safety or advancing sustainable development, discover how IoT can transform your city into a model of urban resilience.
Understanding Smart Infrastructure and IoT
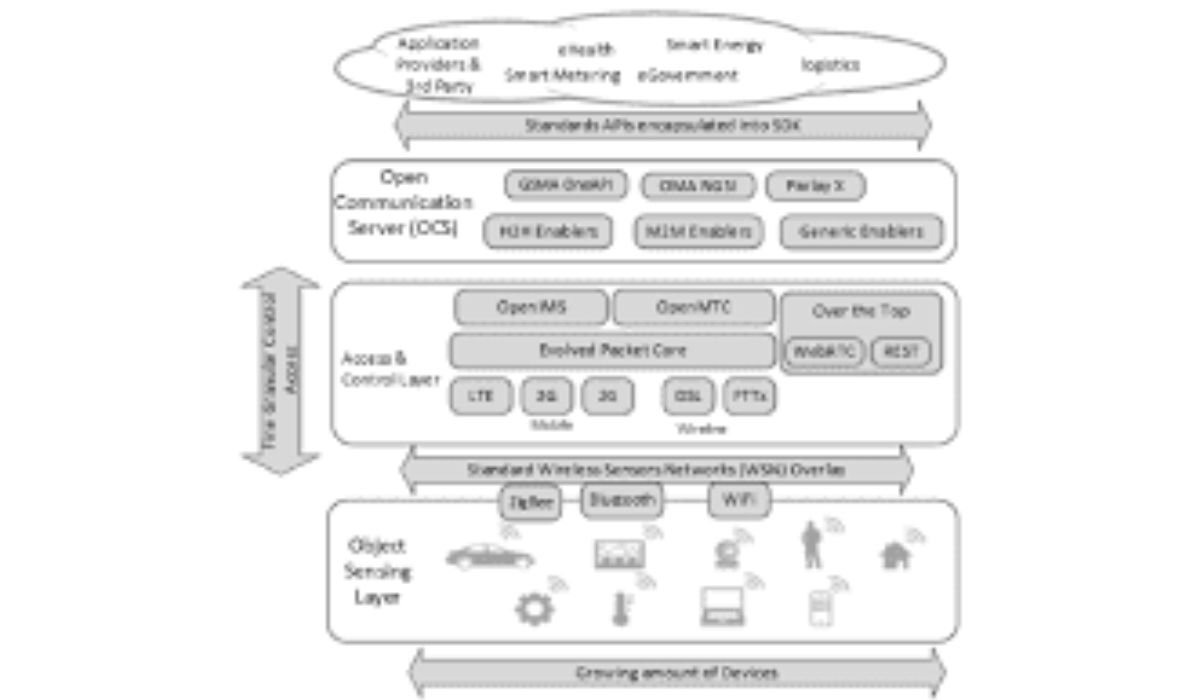
Smart infrastructure refers to the integration of digital technologies into physical urban systems, making them more responsive and efficient. At its core, IoT acts as the nervous system, connecting devices to gather and analyze data in real-time.
What is IoT?
The Internet of Things, or IoT, encompasses a network of interconnected devices embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity. These devices communicate over the internet, enabling automated data exchange without human intervention. In urban contexts, IoT goes beyond gadgets—it’s about creating ecosystems where streetlights adjust based on foot traffic or waste bins signal when they’re full.
Think of IoT as the bridge between the physical and digital worlds. For instance, simple sensors can monitor air quality, while advanced setups use edge computing to process data locally, reducing latency.
Key Components in Urban Settings
Urban IoT relies on sensor networks for data collection, connectivity protocols like LoRaWAN for long-range communication, and data analytics platforms to derive insights. Digital twins—virtual replicas of physical assets—allow planners to simulate scenarios, from traffic patterns to flood risks.
In practice, these components form layered architectures: sensing at the base, networking in the middle, and application layers at the top for decision-making. This setup ensures scalability, even for small cities seeking cost-effective smart infrastructure IoT solutions.
Tangible Benefits of IoT-Driven Smart Infrastructure
IoT isn’t just tech hype; it delivers measurable gains for cities. From reducing operational costs to improving quality of life, the advantages are profound and practical.
Enhancing Public Safety
Public safety tops the list for many municipal leaders. IoT sensors enable real-time traffic management using smart infrastructure, detecting accidents instantly and rerouting vehicles to minimize congestion. In emergency scenarios, connected cameras and gunshot detection systems alert responders faster, potentially saving lives.
Consider how urban automation integrates with public transport: Sensors track bus locations, providing commuters with accurate arrival times and reducing wait-related frustrations. Studies show cities with IoT-enhanced safety see up to 20% drops in response times.
Promoting Sustainable Development
Sustainability is non-negotiable in modern urban planning. IoT supports smart grid systems that optimize energy distribution, cutting waste by monitoring usage patterns. For waste management, sensors in bins notify collection teams only when needed, slashing fuel consumption and emissions.
This ties into broader sustainable development goals, like using IoT for water conservation—detecting leaks in real-time to prevent billions of gallons lost annually. Cities adopting these can achieve 15-30% efficiency gains in resource use.
Improving Municipal Efficiency
Efficiency translates to budget savings—a key concern for local governments. IoT streamlines operations through predictive maintenance: Sensors on bridges or roads flag issues before they become costly repairs.
Data analytics from IoT feeds into dashboards, helping officials make informed decisions on everything from lighting to parking. For smaller municipalities, this means scalable solutions without massive upfront costs, fostering municipal efficiency across the board.
Roadmap for Implementing IoT in Cities
Ready to build resilient infrastructure? Here’s a step-by-step guide tailored for decision-makers balancing innovation with fiscal responsibility.
Step 1: Assess Current Needs and Set Goals
Start by auditing your city’s pain points—traffic bottlenecks, energy inefficiencies, or safety gaps. Engage stakeholders like civil engineers and IT directors to define objectives, such as implementing smart infrastructure IoT in cities for sustainability.
Prioritize based on impact: Focus on high-ROI areas like how IoT improves municipal waste management.
Step 2: Choose the Right Technologies
Select connectivity protocols suited to your environment—LoRaWAN for wide-area coverage or 5G for high-speed needs. Integrate edge computing to handle data locally, reducing reliance on cloud resources.
Budget tip: Opt for modular systems that scale, avoiding vendor lock-in.
Step 3: Pilot and Scale Projects
Launch small pilots, like sensor-equipped streetlights in one district. Monitor metrics: Energy savings, user feedback, and ROI.
Once proven, expand citywide. Involve public-private partnerships to share costs—many tech firms offer incentives for smart city initiatives.
Step 4: Ensure Data Security and Integration
Address securing IoT in cities and connected infrastructure from the outset. Use encryption and regular audits to protect data.
Integrate with existing systems via APIs, creating a unified platform for data analytics.
Step 5: Monitor, Optimize, and Engage Community
Post-implementation, use dashboards for ongoing oversight. Gather resident input to refine systems—transparency builds trust.
Remember, success metrics include not just tech performance but community satisfaction.
This roadmap aligns with the role of 5G in urban smart infrastructure, accelerating connectivity for faster results.
Overcoming Challenges in IoT Adoption
No transformation is without hurdles. Recognizing these ensures smoother implementation.
Security and Privacy Concerns
Data breaches pose risks in connected cities. Securing IoT in cities demands robust protocols—multi-factor authentication and AI-driven threat detection.
Privacy laws like GDPR guide ethical data use, balancing innovation with citizen rights.
Infrastructure and Scalability Issues
Aging infrastructure can hinder integration. Solutions include retrofitting with wireless sensors to minimize disruption.
For scalability, adopt open standards to avoid silos, ensuring systems grow with urban demands.
Cost and Adoption Barriers
Budgets constrain many cities. Start with cost-effective smart infrastructure IoT solutions for small cities, leveraging grants or phased rollouts.
Overcome resistance through training and demonstrating quick wins, like reduced maintenance costs.
Recent trends show declining sensor prices, making IoT more accessible.
Real-World Case Studies
Learning from pioneers accelerates progress. Dallas’s Smart Dallas Roadmap uses IoT for traffic and energy management, achieving notable efficiency gains.
In Singapore, IoT sensors monitor environmental factors, enhancing urban resilience against climate events. Outcomes include 25% better resource allocation.
Barcelona’s smart lighting reduced energy use by 30%, proving IoT’s ROI in sustainable development.
These examples highlight benefits of IoT in cities for local government, from cost savings to improved services.
| City | IoT Application | Key Benefit | ROI Timeline |
| Dallas | Traffic & Energy Management | 20% Efficiency Increase | 2 Years |
| Singapore | Environmental Monitoring | Enhanced Resilience | 18 Months |
| Barcelona | Smart Lighting | 30% Energy Savings | 1 Year |
| Amsterdam | Waste Management | Reduced Collection Costs | 15 Months |
Future Trends in Smart Urban Infrastructure
Looking ahead, urban resilience through IoT will leverage AI for predictive analytics, foreseeing issues like infrastructure failures.
5G integration will enable ultra-low latency, supporting autonomous vehicles and advanced digital twins.
By 2025, over 500 cities may use digital twins for planning, per industry insights. Edge AI will process data closer to sources, boosting efficiency.
Sustainability trends include IoT for circular economies, recycling resources intelligently.
As urban automation evolves, expect seamless integration with blockchain for secure data sharing.
In summary, smart infrastructure: IoT in Cities offers a pathway to resilient, efficient urban futures. Key benefits include enhanced public safety, sustainable resource use, and operational savings—achievable through a structured roadmap that addresses challenges like security and costs. For stakeholders, the time to act is now: Consult experts or pilot projects to harness IoT’s potential. Explore resources from organizations like the EPA for stormwater innovations or link to our guide on “Urban Drainage Systems” for related insights. Transform your city today.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE: Architecture of Urban Landscapes: The Blueprint for Better Cities